-
Posted By drruby.Sachdev@gmail.com
-
-
Comments 0
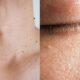
When it comes to skin concerns, two conditions that frequently arise are hyperpigmentation and melasma. Despite their prevalence, many individuals are unaware of the key differences between melasma and hyperpigmentation, leading to confusion in identifying and treating these issues. Hyperpigmentation vs. melasma is a common topic of discussion among skincare enthusiasts, as both conditions involve darkening of the skin but have distinct causes and characteristics.
Hyperpigmentation refers to areas of skin that become darker than the surrounding skin due to an excess production of melanin. This condition can result from various factors such as sun exposure, inflammation, and skin injuries. Hyperpigmentation can appear anywhere on the body, with hyperpigmentation on the forehead being particularly common.
On the other hand, melasma is a chronic skin disorder that causes dark, discolored patches, primarily on the face. The melasma meaning is often tied to hormonal changes, which can be triggered by pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy. These dark patches are typically symmetrical and more prominent in individuals with darker skin tones.
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation refers to areas of skin that become darker than the surrounding skin due to an excess production of melanin. This condition can affect various parts of the body and is often seen on the face, neck, and hands. Hyperpigmentation on the forehead, for example, is a common concern for many.
What Is Melasma?
Melasma, meaning a chronic skin disorder, manifests as dark, discolored patches on the skin. This condition is distinct from general hyperpigmentation due to its specific triggers and presentation. The key difference between melasma and hyperpigmentation lies in their causes: melasma is primarily induced by hormonal changes, making it particularly prevalent in women. These hormonal fluctuations can be due to pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy, often earning melasma the nickname “the mask of pregnancy.”
Melasma typically appears on areas of the face that are frequently exposed to the sun. Common sites include the cheeks, bridge of the nose, forehead, chin, and above the upper lip. These patches are usually symmetrical and can range in color from light brown to darker brown or grayish. The condition is more noticeable in individuals with darker skin tones but can affect all skin types.
Understanding hyperpigmentation vs. melasma is crucial for appropriate treatment. While both conditions involve darkened skin, melasma’s hormonal component requires targeted management. Treatments for melasma often include sun protection, as UV exposure can exacerbate the condition, as well as topical treatments like hydroquinone and corticosteroids. Procedures such as microneedling
Key Differences Between Hyperpigmentation vs Melasma
Causes
The primary difference between melasma and hyperpigmentation lies in their causes. Hyperpigmentation results from an overproduction of melanin due to factors such as sun exposure, inflammation, or skin injuries. Prolonged sun exposure stimulates melanin production, leading to dark spots, while inflammation from acne or other skin conditions can also trigger hyperpigmentation. Additionally, any form of skin trauma, like cuts or burns, can result in localized darkening as the skin heals.
On the other hand, melasma is primarily influenced by hormonal changes, often exacerbated by sun exposure and certain medications. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, the use of birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy can trigger melasma. These hormonal changes stimulate melanocytes, the cells responsible for melanin production, causing dark patches to form, especially on sun-exposed areas of the face.
Appearance
Another key difference between melasma and hyperpigmentation is their appearance. Melasma typically presents as larger, more symmetrical patches of darkened skin. These patches are often found on both sides of the face in a mirror-like pattern, commonly on the cheeks, bridge of the nose, forehead, chin, and above the upper lip.
In contrast, hyperpigmentation can appear as smaller, irregular spots or patches. These spots can vary in size and shape and are not usually symmetrical. Hyperpigmentation can develop anywhere on the body, making it less predictable in its pattern and distribution compared to melasma.
Affected Areas
Melasma vs. hyperpigmentation also differ in the areas they affect. Melasma predominantly affects the face, particularly the cheeks, forehead, nose, chin, and above the upper lip. This facial distribution is partly due to the condition’s sensitivity to hormonal changes and sun exposure.
Hyperpigmentation, however, can occur anywhere on the body. Common sites include the face, neck, hands, and other areas frequently exposed to the sun. Hyperpigmentation can also develop on areas of the skin that have experienced trauma or inflammation, making its potential locations more diverse.
Population
The population affected by hyperpigmentation melasma tends to vary. Hyperpigmentation is more common in individuals with darker skin tones, as they have more active melanocytes, making their skin more prone to developing dark spots. It can affect people of all ages and genders, resulting from various external factors like sun exposure and skin injuries.
Melasma, however, is particularly prevalent among pregnant women, earning it the nickname “the mask of pregnancy.” Women on birth control pills or those undergoing hormone replacement therapy are also at higher risk. The hormonal component of melasma makes it more common in women than in men, though it can still affect both genders.
Understanding these key differences between hyperpigmentation and melasma is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Recognizing the distinct causes, appearances, affected areas, and populations helps in tailoring appropriate skincare routines and treatments for each condition.
Treatment Options
Hyperpigmentation Treatment
1. Topical Treatments:
Retinoids and hydroquinone are commonly used to address hyperpigmentation. Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, work by increasing cell turnover, while hydroquinone inhibits melanin production. These ingredients can help lighten dark spots and promote an even skin tone when applied regularly as part of a skincare routine.
2. Chemical Peels:
Chemical peels involve applying a solution containing acids such as glycolic acid, salicylic acid, or lactic acid to the skin. These acids exfoliate the top layers of the skin, removing dead cells and stimulating collagen production. Chemical peels can help reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation by promoting skin renewal and improving overall skin texture.
3. Laser Therapy:
Laser therapy, or laser skin resurfacing, is an advanced treatment option for hyperpigmentation. This procedure uses focused laser beams to target and break down melanin deposits in the skin. Laser therapy can effectively reduce pigmentation and improve skin tone and texture with minimal downtime. Different types of lasers, such as fractional lasers or intense pulsed light (IPL) devices, may be used depending on the specific needs of the patient.
Melasma Treatments
1. Sun Protection:
Sun protection is essential for managing melasma and preventing its worsening. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with high SPF daily helps shield the skin from harmful UV rays, which can trigger melasma flare-ups. Additionally, wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses can further minimize sun exposure and protect the skin from damage.
2. Topical Treatments:
Hydroquinone and corticosteroids are commonly prescribed topical treatments for melasma. Hydroquinone works by inhibiting melanin production, while corticosteroids help reduce inflammation and hyperpigmentation. These topical agents are usually applied directly to the affected areas of the skin and may be used in combination with other treatments for optimal results.
3. Procedures:
Procedures such as microneedling and laser therapy can also be effective in treating melasma. Microneedling involves using a device with fine needles to create tiny punctures in the skin, stimulating collagen production and improving skin texture. Laser therapy targets melanin deposits in the skin, breaking them down and reducing pigmentation. These procedures can help improve the appearance of melasma and promote overall skin rejuvenation when performed by a qualified skincare professional.
Understanding the available treatment options for hyperpigmentation and melasma is essential for effectively managing these skin concerns. By addressing the underlying causes and choosing appropriate therapies, individuals can achieve clearer, more radiant skin and regain their confidence. Consulting with a dermatologist or skincare specialist can help determine the best course of action based on individual skin type, concerns, and treatment goals.
Prevention Tips
Preventing hyperpigmentation and melasma requires a proactive approach to sun protection and skincare. Daily application of a broad-spectrum sunscreen, with an SPF of 30 or higher, is crucial to shield the skin from harmful UV rays that can trigger both conditions. Even on cloudy days, UV radiation can penetrate the clouds and cause damage to the skin, so sunscreen should be applied year-round.
In addition to sunscreen, wearing protective clothing such as hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves can further minimize sun exposure. Seeking shade during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., can also reduce UV exposure and lower the risk of developing hyperpigmentation and melasma.
Incorporating skincare products containing key ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, and retinoids into your daily routine can help maintain an even skin tone and prevent dark spots from forming. Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant, protecting the skin from environmental damage and brightening the complexion. Niacinamide, also known as vitamin B3, helps regulate melanin production and improve skin texture. Retinoids promote cell turnover and collagen production, leading to smoother, more radiant skin.
When to See a Doctor?
If you observe stubborn dark spots or patches on your skin that do not respond to over-the-counter treatments, it is advisable to seek professional help from a dermatologist. Dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating various skin conditions, including hyperpigmentation and melasma. They can provide an accurate diagnosis, determine the underlying cause of your skin concern, and recommend personalized treatment options tailored to your specific needs. By consulting a dermatologist, you can receive expert guidance and access to advanced treatments that may effectively address your hyperpigmentation or melasma, helping you achieve clearer and healthier skin.
Why To Choose Skinnfit Medspa for Treatments?
SkinnFit Medspa, under the expert guidance of Dr. Ruby Sachdev, is a premier hair and skin treatment clinic located in Bengaluru, Karnataka. With a focus on providing comprehensive solutions for various skin concerns, including hyperpigmentation and melasma, SkinnFit Medspa stands out for its commitment to personalized care and cutting-edge treatments.
At SkinnFit Medspa, clients benefit from the expertise of experienced dermatologists who employ the latest technology and techniques to deliver optimal results. Dr. Ruby Sachdev and her team understand the nuances of hyperpigmentation vs. melasma, ensuring accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans for each individual.
Conclusion
Differentiating between melasma and hyperpigmentation is crucial for effectively managing these skin conditions. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and suitable treatments for each, individuals can take proactive measures to achieve a clearer and more radiant complexion.
Melasma, influenced by hormonal changes, often presents as symmetrical patches on the face, while hyperpigmentation can occur due to various factors such as sun exposure and skin trauma, resulting in irregular dark spots. Recognizing these distinctions enables tailored treatment approaches.
If you’re facing challenges with your skin, whether it’s melasma, hyperpigmentation, or any other concern, seeking professional guidance is essential. Dermatologists, like those at Skinnfit, can provide accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans to address your specific needs effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Melasma typically appears as larger, symmetrical patches on the face, especially on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and above the upper lip. In contrast, hyperpigmentation presents as smaller, irregular spots or patches on the skin. If you notice darkened areas on your face that are symmetrical and become more prominent with sun exposure or hormonal changes, it is likely melasma. However, if the dark spots are irregular in shape and not necessarily symmetrical, it may be hyperpigmentation.
Melasma can be challenging to treat and may require ongoing management, but it is not necessarily permanent. With proper skincare and treatment, including sun protection and topical therapies, melasma can improve over time. However, some individuals may experience recurrent flare-ups, especially with sun exposure or hormonal changes.
Individuals with darker skin tones are more prone to hyperpigmentation due to increased melanin production. However, hyperpigmentation can affect people of all skin types and ethnicities, particularly those with a history of sun exposure, skin trauma, or inflammation.
While diet alone may not directly cause hyperpigmentation or melasma, certain dietary factors can influence skin health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can support overall skin health and may help reduce the risk of hyperpigmentation and melasma. Additionally, staying hydrated and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to healthier skin.
Sun exposure is a significant trigger for both hyperpigmentation and melasma. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation stimulates melanin production in the skin, leading to darkening of existing pigmentation and the formation of new spots. Individuals with melasma are particularly sensitive to sun exposure, as UV rays can exacerbate the condition and cause flare-ups. Therefore, wearing sunscreen daily and minimizing sun exposure are essential for preventing and managing hyperpigmentation and melasma.
Hyperpigmentation and melasma can affect individuals of all skin types, but they may present differently depending on skin tone. In darker skin tones, hyperpigmentation and melasma may appear more pronounced due to increased melanin production. Additionally, treatment approaches may vary based on skin type, with some therapies being more suitable for certain skin tones than others. It’s essential to consult with a dermatologist who can tailor treatment plans to individual skin types and concerns.
Recent Posts
- Bangalore Monsoon Skin SOS: Dr Ruby Sachdev’s Tips to Beat Seasonal Breakouts
- Stretch Marks Demystified: Only These Treatments Really Fade Them—Here’s Why
- Dry Scalp vs. Dandruff? Spot the Difference & End the Itch for Good
- 🧴 Pollution + UV in Bangalore? Why Sunscreen Alone Isn’t Enough—Your Complete Daily Skin Defense
- Glass Skin Treatment in Bangalore: Is It Worth the Hype?